Polio is targeted for eradication because the presence of the virus anywhere means that children everywhere are at risk. The Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI) focuses on strengthening Acute Flaccid Paralysis (AFP) surveillance worldwide to detect and respond to the poliovirus, to build herd immunity to protect the population and to halt the transmission of the virus. The data on the spread of AFP is invaluable especially for polio-endemic countries like Afghanistan, Pakistan, and Nigeria because it helps in determining whether they can finally be certified polio-free.
There are four steps involved in AFP surveillance and the Auto- Visual AFP Detection and Reporting (AVADAR) project responds to the first step—finding and reporting children with AFP—in eight priority countries in Africa. In many of these countries, disease surveillance and notification officers (DSNOs) at the health facilities are unable to actively find AFP cases for reasons ranging from difficulty in accessing settlements to security challenges. AVADAR trains community informants to search for and report the presence and/or absence of children with AFP in their community, using a mobile application. The application also has an embedded video that shows a child with AFP so that community informants can better recognize an AFP case. This reduces the burden on the DSNOs and allows them to focus on confirming if the case is truly AFP or not.
How AVADAR works
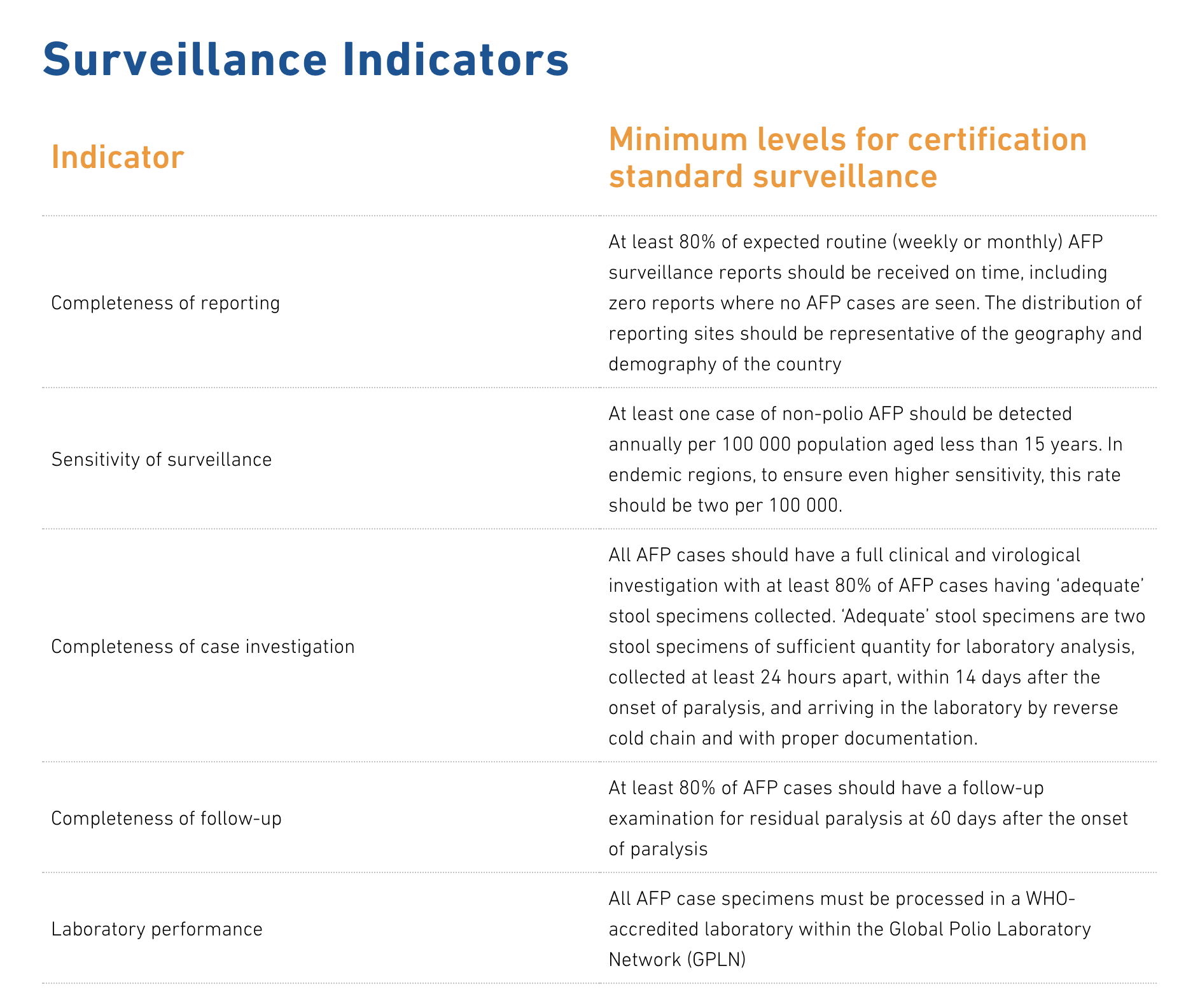
To ensure that AFP surveillance is conducted impactfully and that the AFP surveillance data collected is accurate, timely and of high quality, the GPEI defined five global indicators: Completeness of reporting, Completeness of case investigation, Completeness of follow-up, Sensitivity of surveillance and Laboratory performance.
Global Polio Eradication Initiative: AFP Surveillance indicators
AVADAR was designed by eHealth Africa, Novel-T, the World Health Organization (WHO) and other partners, to contribute to the achievement of the above targets. Below are the measures that have been put in place to ensure the collection and use of high-quality data to track and reports suspected AFP cases, and to inform decision making for polio eradication.
Coverage: To decide where to site an AVADAR system, WHO carries out an assessment of the target country/districts to identify rural, hard-to-reach and underserved communities which are typically more predisposed to poliomyelitis. The AVADAR system, equipped with geospatial tracking capabilities is then deployed to community informants/ AFP reporters. This unique feature of the application helps to validate the location of the suspected AFP case, independent of the reporter.
Reporting: The AVADAR application allows informants to deliver reports anywhere and anytime in order to prevent data loss and to ensure near real-time, accurate reporting. The app is designed to be used by people with basic literacy levels and is available in eighteen local African languages for ease of understanding. A report is better able to provide insight and enhance planning or decision making when it is timely. One of the key weekly metrics captured on the AVADAR dashboard is the number of complete results that were submitted as at when due, thus ensuring that all informants are actively engaged. Informants are expected to look out for and report cases of children aged 15 years and below, who have any form of physical deformity on the limbs or arms. In the event that no AFP case has been sighted within a week, the informant must send a ‘no report’, to validate his presence on the system.
AVADAR has improved the rate of AFP reporting compared to the traditional system of AFP reporting. For example, between June 2017 and June 2018 in the Lake Chad Basin countries(Chad, Niger, Nigeria, and Cameroon), the AVADAR system recorded 589 supsected cases against the 213 cases recorded by the traditional AFP Surveillance system.
Verification: Paralysis in children can be caused by several agents including the Poliovirus. After the community informants submit their reports of suspected AFP cases, trained health workers carry out further investigations to confirm if they are true AFP cases. The WHO has designated laboratories all over target countries that are certified to test fecal samples and isolate the poliovirus. AVADAR weekly reports show how many suspected AFP cases were reported, how many were tested and the number of cases confirmed to be true AFP cases. This sort of data measures the cost of a single confirmed AFP case, the prevalence and incidence of AFP in target areas, thus enhancing the quality of AFP surveillance data for decision making.
AVADAR dashboard
Having data on the spread of AFP in a geographic location helps with planning towards its containment. Since Poliomyelitis is mainly oral-fecally transmitted, sanitization and sensitization of the environment and inhabitants respectively can help reduce the spread of polio. AFP data gathered across different locations has been used in making an informed decision on determining the number of health workers that can effectively manage its spread to neighboring communities. On the contrary, no data or false data could lead to health workers focusing their energy in wrong locations thereby risking the spread of polio and the extension of its existence.
Without reliable and accurate AFP surveillance data, true progress towards polio eradication cannot be measured. AVADAR’s impact in high-risk countries across Africa demonstrates how context-appropriate interventions and solutions can transform disease surveillance and emergency management systems.
“One of the most important features of the AVADAR system is the engagement of over a hundred community informants per county. They are trained and equipped for the first time to provide timely reports that can be accessed at all levels from the county to the national level and beyond, thereby allowing suspected cases to be investigated in an accurate and efficient way.”