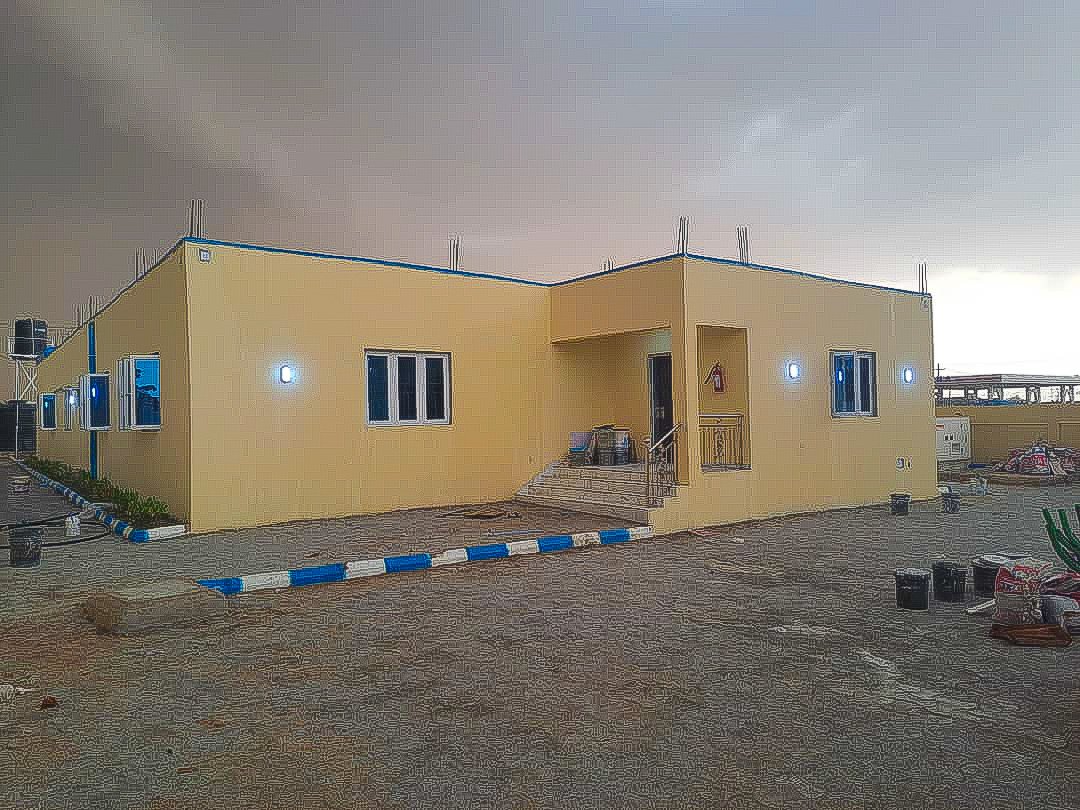
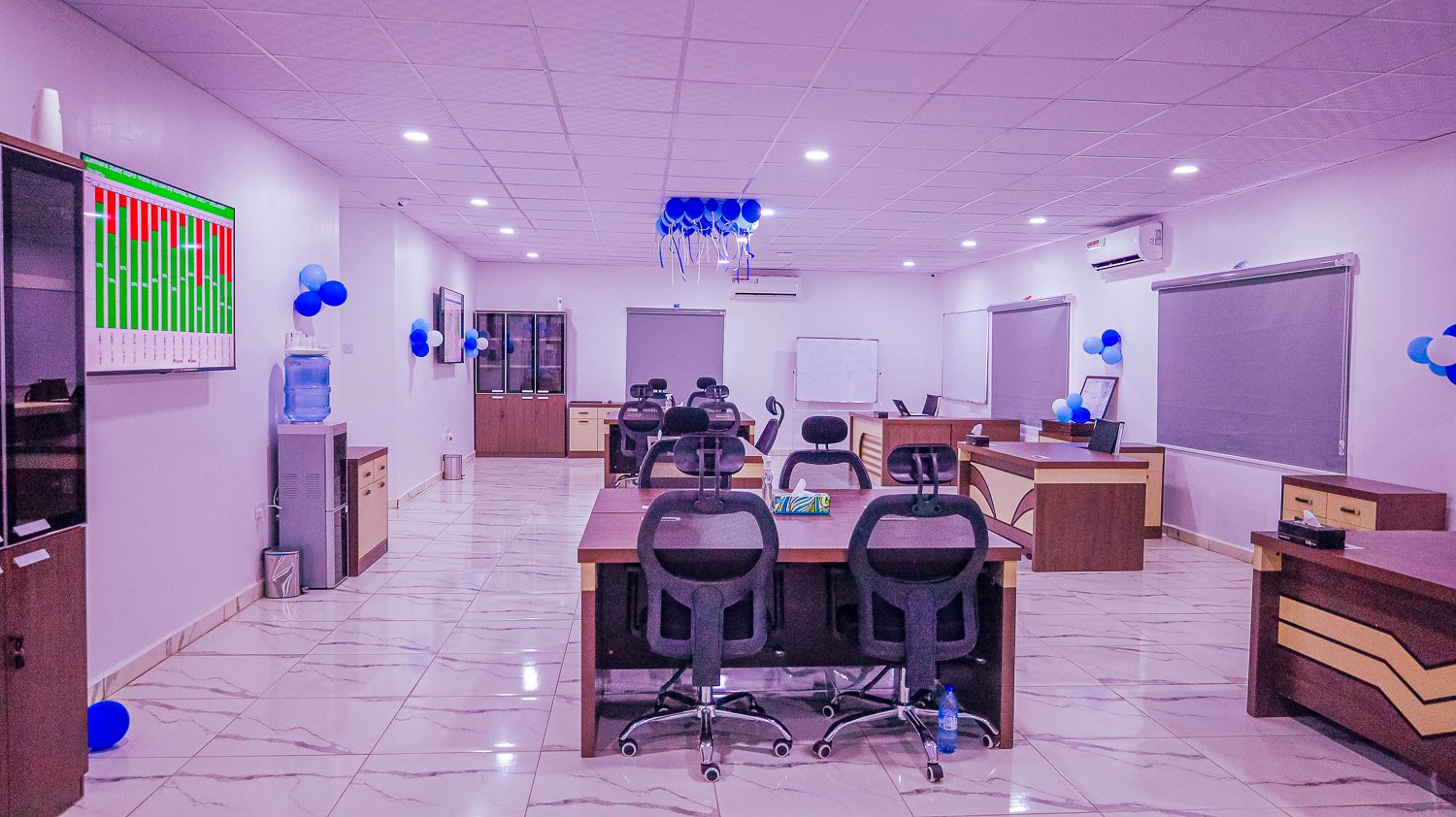
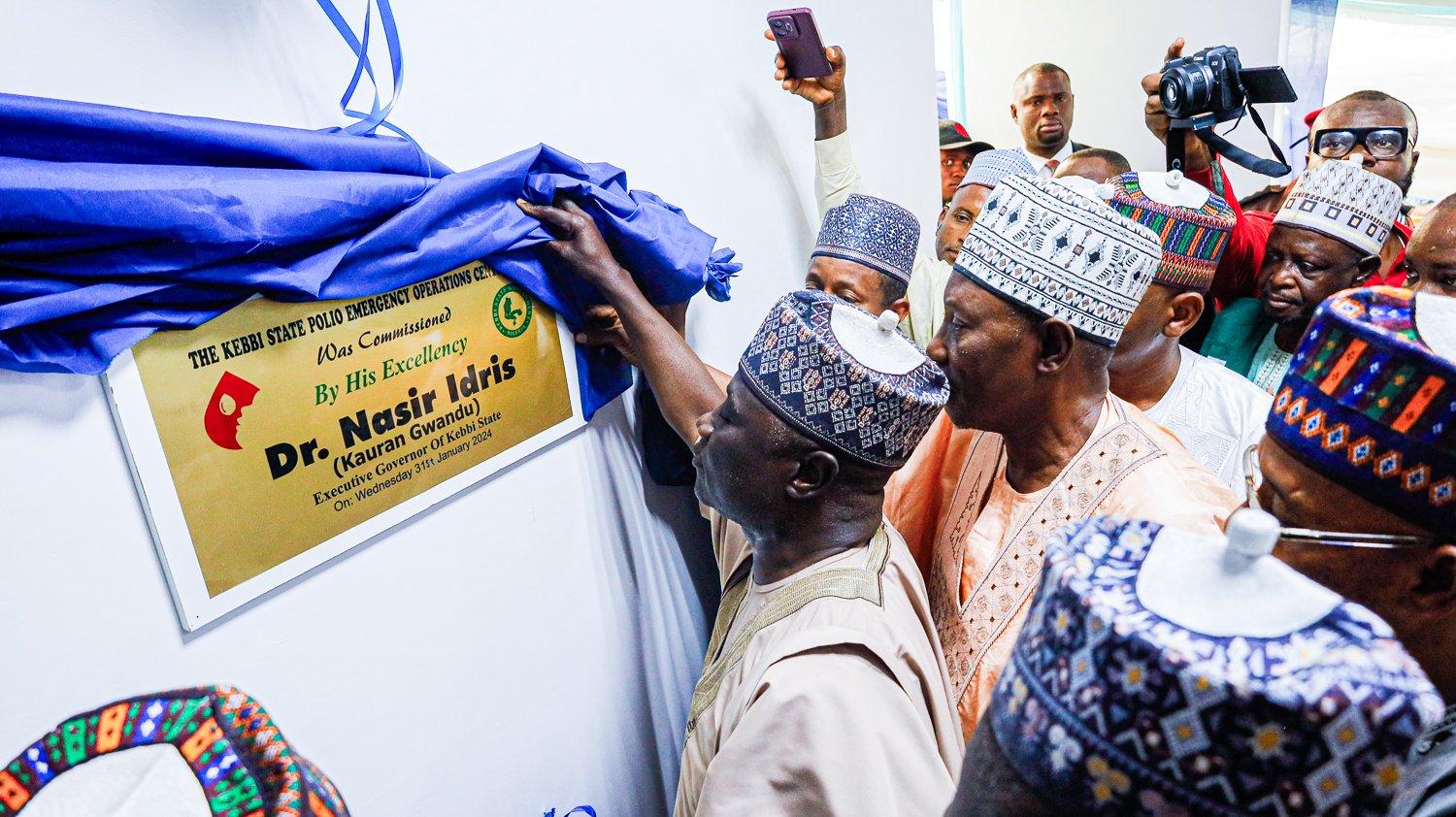
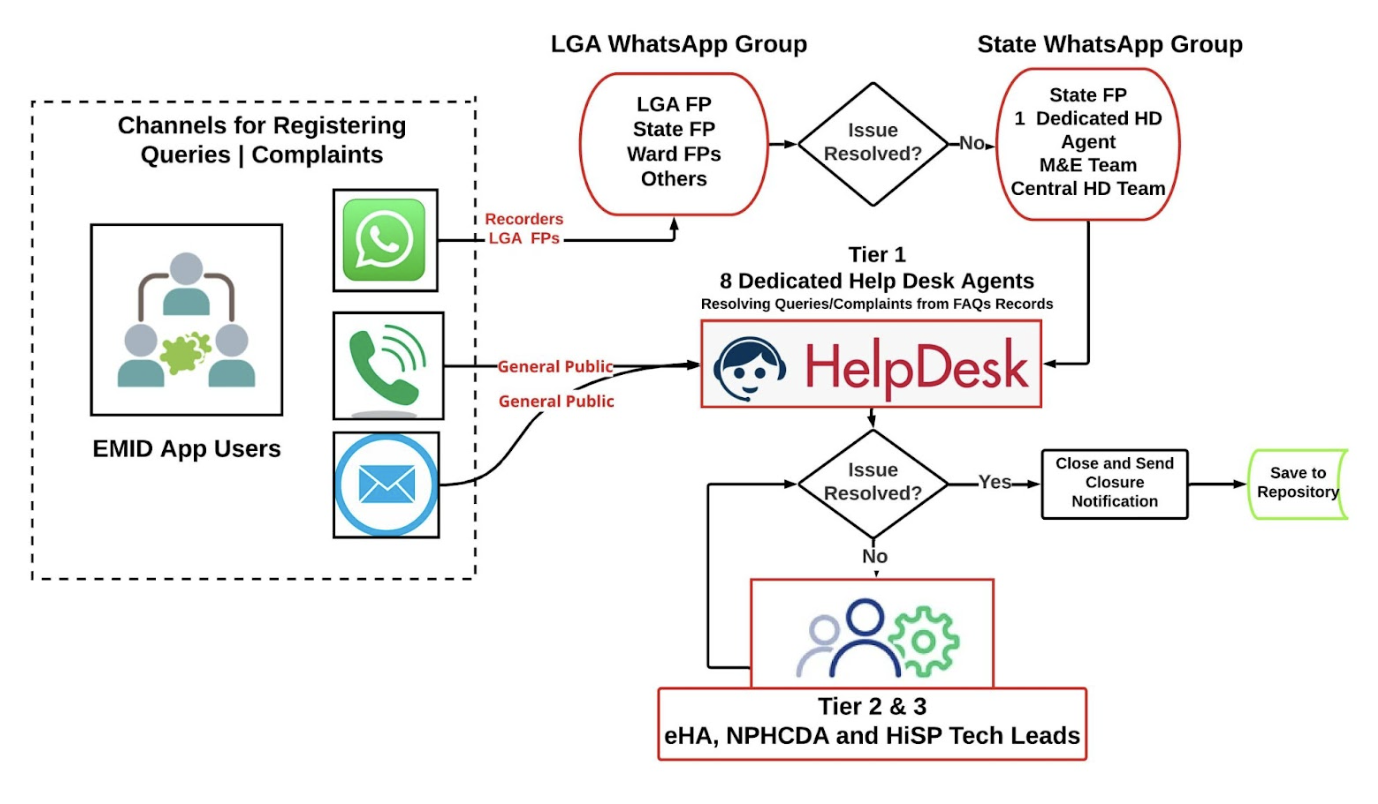
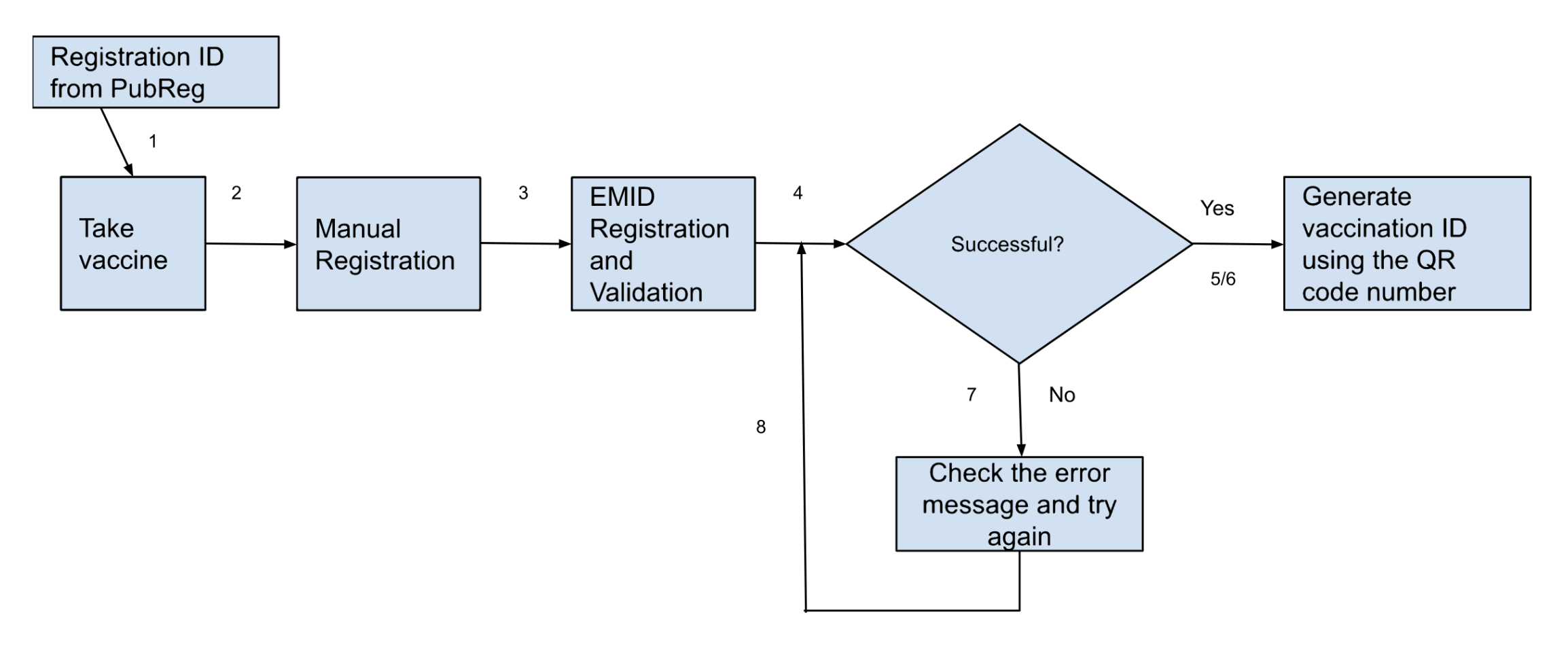
Following the successful commissioning of the Emergency Operations Centers (EOCs) in Kebbi and Zamfara states earlier this year, the spotlight now shines on Niger State as they prepare to inaugurate their own EOC, marking the 11th such facility constructed and overseen by eHealth Africa across Nigeria.
The inclusion of Niger State in this initiative can be traced to the state being one of the critical regions in Nigeria's fight against the circulating variant of the polio virus and other vaccine-preventable diseases. Aligned with the objectives of the Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI) and its partners, this new EOC aims to enhance coordination and response strategies for Niger State.
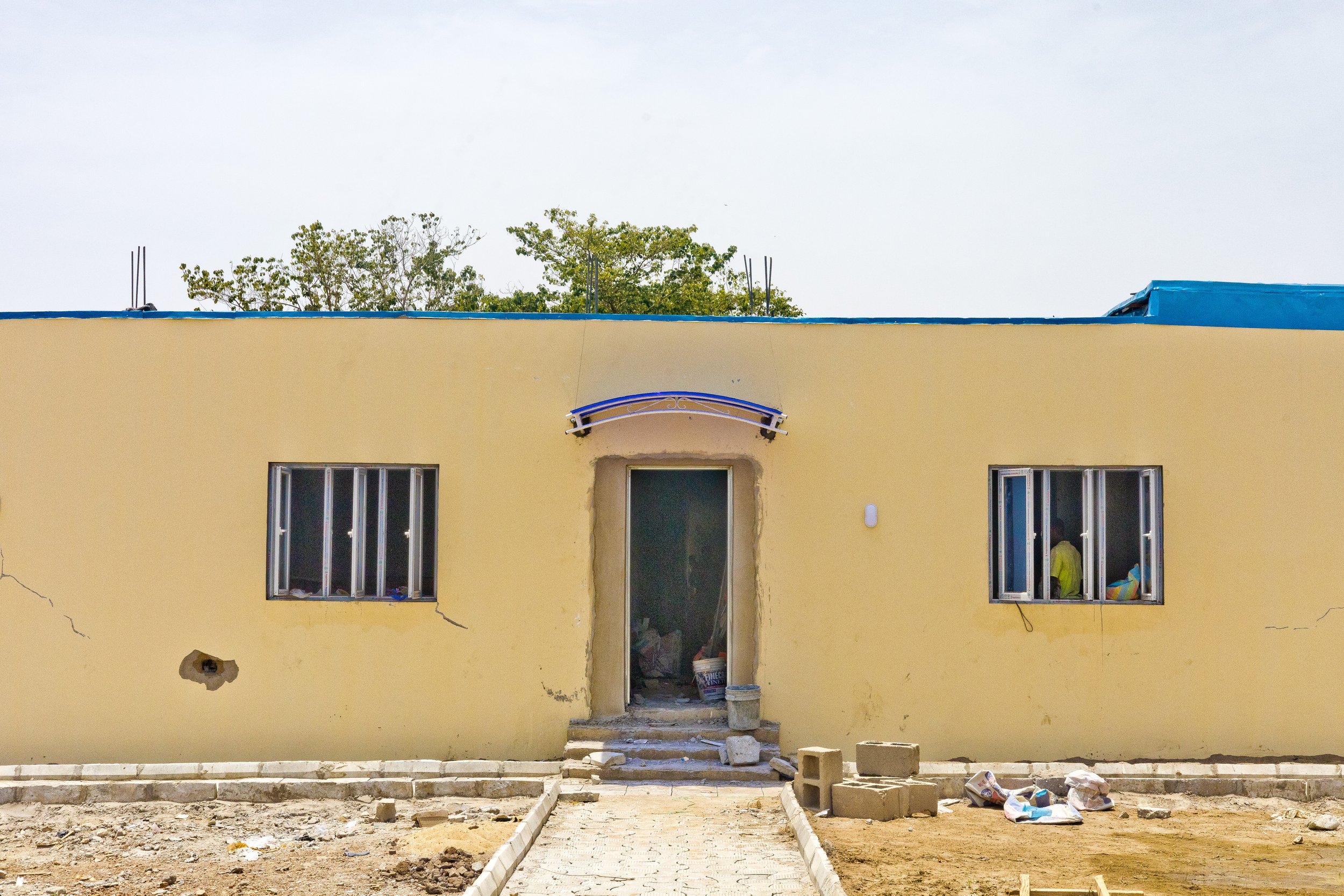
Upon its completion, health stakeholders anticipate a state-of-the-art infrastructure that will streamline the planning and execution of public health interventions in Niger State. Through data-driven decision-making processes, the EOC promises to yield improved outcomes, benefiting not only the citizens of Niger State but also its neighboring regions.
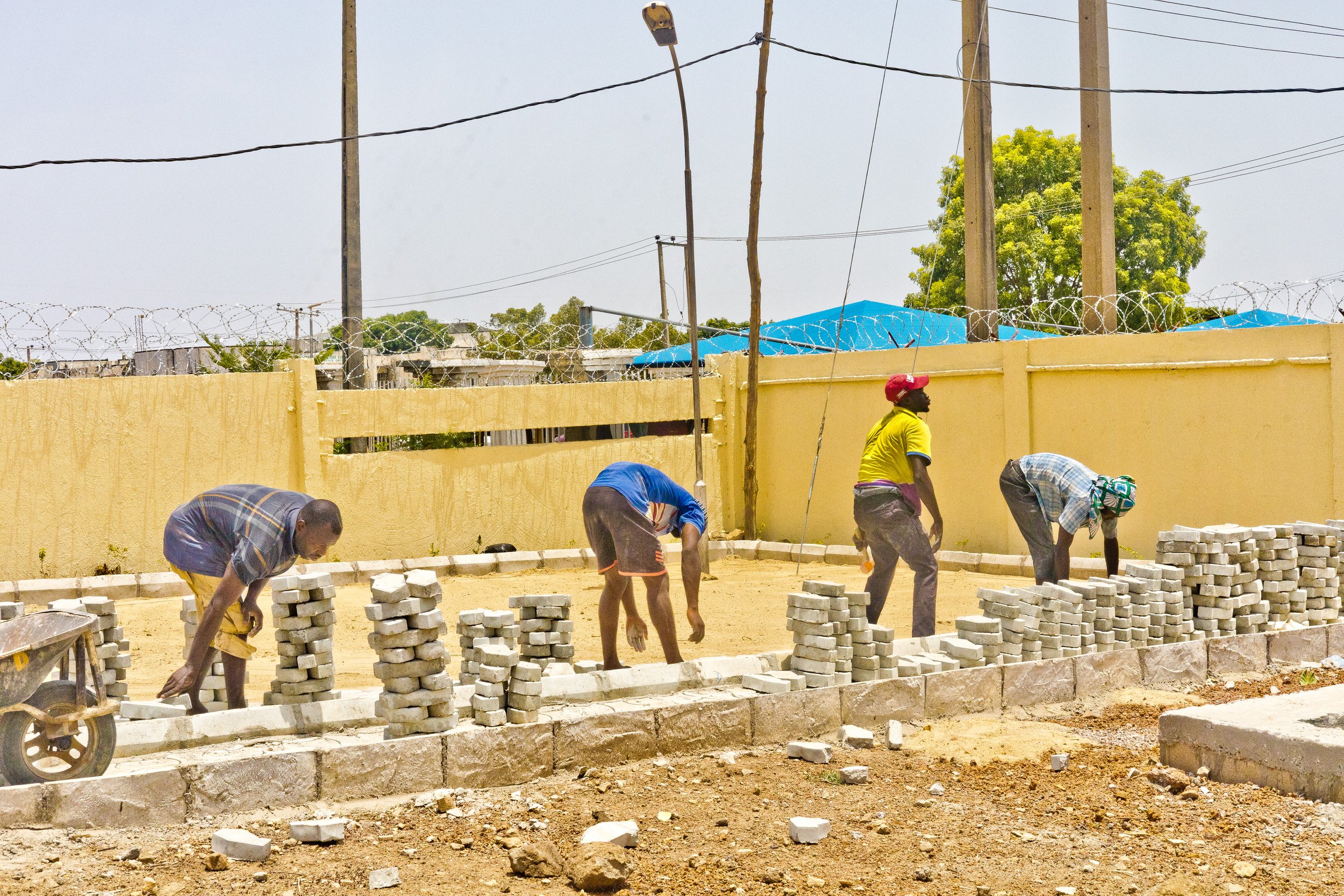
During a recent site inspection, discussions with key figures including Eyitayo Samuel, the supervisory site manager, Dr. Abdullahi Usman Imam, Permanent Secretary of the Niger State Ministry of Public Health Care (NSMPHC), and Dr. Samuel Jiya, Director of Disease Control and Immunization at NSMPHC, shed light on the construction progress, and future collaboration prospects.
Eyitayo Samuel, the supervisory site manager, shared insights into the construction progress, affirming the dedication to quality and functionality. He stated, "The progress of the work reflects meticulous planning and execution, indicating a facility that is poised to meet its objectives effectively."
Dr. Ibrahim Ahmed Dangana, the Honourable Commissioner for Primary Health Care Development in Niger State, along with Dr. Abdullahi Usman Imam, Permanent Secretary of NSMPHC, Dr. Samuel Jiya, Director of Disease Control and Immunization, and other essential stakeholders, conducting a site inspection of the ongoing construction of the Niger State Emergency Operation Center.
Dr. Abdullahi Usman Imam commended the meticulous planning evident in the design phase of the EOC, foreseeing its potential to significantly enhance primary healthcare services in Niger State. He affirmed the government's commitment to maintaining the facility at world-class standards, allocating resources for its upkeep and even planning to establish a Data Center to complement its activities. Dr. Abdullahi Usman Imam remarked, "Looking at the progress of the work, it is obvious that a lot of planning has gone into the design phase, as It is already looking like a world class facility that would serve the purpose for which it is being built thereby making very significant impact on Primary Health care services in Niger state."
He further stated, "The government of Niger state will ensure that a budget is set aside to ensure that the facility is maintained to world class standard. The government of Niger state has already set aside in its budget for this year to establish a Data center, this will complement the activities of the EOC."
Dr. Samuel Jiya emphasized the EOC's role in fortifying the state's immunization campaigns, likening them to strategic warfare where planning and execution are paramount. With the EOC as the central hub for coordination, he expressed confidence in the state's ability to combat prevailing diseases effectively. Dr. Samuel Jiya stated, “The campaigns are like a war situation whereby a lot of planning and strategizing goes into play, and this EOC as well equipped would be the hub of that planning and strategizing, ensuring that we efficiently fight the existing variant of polio and other vaccine-preventable diseases, and kick them out of the state.”
The construction and management of the Niger State EOC by eHealth Africa, with support from The Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation and Aliko Dangote Foundation, exemplify the potential for impactful achievements when communities, leaders, and partners unite for public health initiatives.